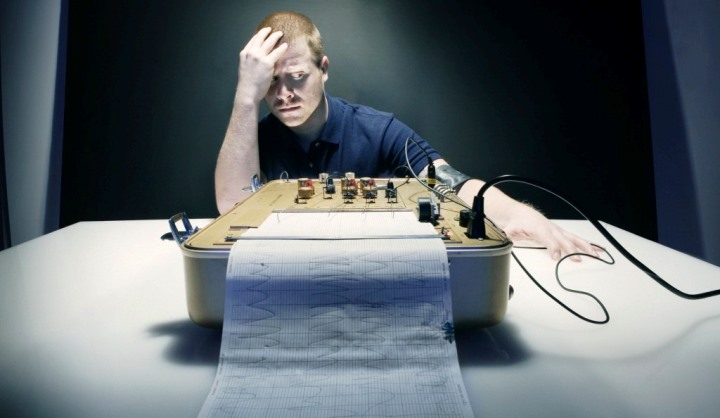
The lie detector, or polygraph, has been the subject of much debate and interest for decades. It is a device designed to detect deception by measuring a person's physiological reactions. In our article, we have collected 10 interesting facts about the lie detector that will help you better understand how this device works and where it is used.
The polygraph records several physiological indicators, such as:
- Blood pressure;
- Heart rate;
- Breath;
- Skin conductivity (galvanic skin response).
These data are recorded at the moment when the subject is asked questions. The idea is that when a person lies, their body reacts with stress, which is reflected in changes in these indicators.
1. History of the invention of the lie detector
The first lie detector was invented in 1921 by John Larson, a police officer from Berkeley, California. His goal was to improve crime investigation methods. Larson developed a machine that measured a suspect’s blood pressure and respiration. This early prototype became the basis for modern polygraphs, which add measurements of such parameters as pulse and galvanic skin response.
Interesting fact:
Larson was against using his invention for mass testing, as he believed that the lie detector could not give an absolute answer about a person's guilt or innocence.
2. Operating principle of the KGR
One of the key indicators that the polygraph measures is the galvanic skin response (GSR). This is the electrical activity of the skin, which changes depending on the emotional state of the person. When a person is stressed or worried, their skin begins to secrete more sweat, which increases electrical conductivity.
Important points:
- The reaction occurs when emotional changes occur;
- Measured using electrodes attached to the skin;
- One of the most reliable indicators of stress.
3. Polygraph in criminology
The polygraph is widely used in criminology and crime investigations. However, the polygraph does not provide direct evidence of guilt or innocence, but only helps investigators narrow the circle of suspects and obtain additional data.
How does a polygraph help in an investigation:
- Assessing the honesty of testimony;
- Reducing the number of suspects;
- Identifying potential motives.
4. Lie detector and military intelligence services
The polygraph is widely used in military and intelligence services to screen job candidates or to investigate incidents involving leaks of classified information. For example, in the United States, employees of the CIA, FBI, and some other intelligence agencies may undergo a polygraph test as part of the hiring process or during regular checks. This allows identifying potential threats to national security and assessing the loyalty of employees.
The main purposes of polygraph testing in military structures are:
- Checking the honesty and reliability of employees;
- Identification of possible connections with foreign intelligence agencies;
- Preventing leaks of classified information.
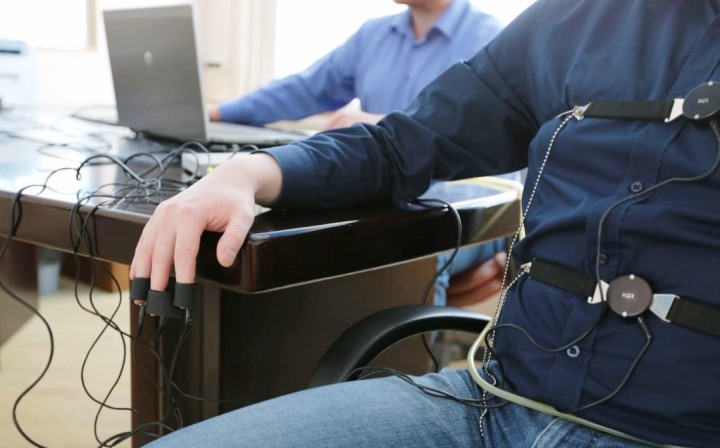

5. Polygraph and scientific research
The scientific community is still debating the effectiveness of the polygraph. While some studies confirm its ability to record physiological changes, others emphasize that there is no 100% guarantee of detecting lies. This is due to the fact that physiological reactions can be caused not only by lies, but also by stress, fear, or other factors.
Scientific findings about the polygraph:
- The polygraph records physiological reactions, but not lies directly;
- Studies show conflicting results;
- Developments to improve accuracy are ongoing.
6. Polygraph in medicine
The polygraph can be used not only to detect lies, but also in medical research. Its ability to measure physiological parameters makes it a useful tool for diagnosing stress conditions, anxiety disorders, and other psychological problems.
Application of polygraph in medicine:
- Diagnosis of anxiety disorders;
- Study of the body's response to stress;
- Study of emotional states.
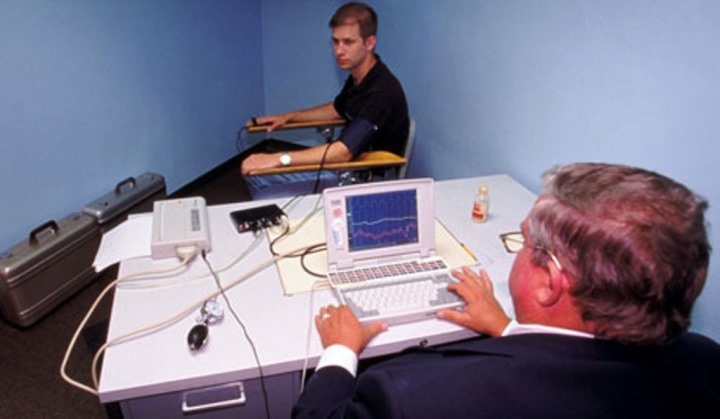

7. The lie detector is used in TV shows
The lie detector often becomes a part of entertainment shows, where it is used to determine the truth among participants. In such programs, viewers are shown how people answer personal or uncomfortable questions, and then, based on the polygraph data, assumptions are made about whether they are telling the truth. Despite the element of show and entertainment context, many viewers are interested in how reliable the results of such tests can be considered.
Examples of popular shows using a polygraph:
- "Secrets on the Lie Detector"
- "Moment of Truth"
- "Let's get married!"
8. The polygraph is not used in the courts of many countries.
Despite the polygraph's popularity, its results are not accepted as evidence in the judicial system of many countries. This is due to the high probability of errors and manipulation of testimony. For example, in the United States, polygraph results are rarely accepted in court, with the exception of some states and with the consent of both parties.
Countries where the polygraph is used or banned:
| Country | Status of polygraph use in courts |
|---|---|
| USA | Limited use |
| United Kingdom | Not accepted as evidence |
| Russia | Used in investigations but not in court. |
| Japan | Used in some cases |
9. Popularity of polygraph testing services
Today, polygraph testing services are becoming increasingly popular among both individuals and businesses. Companies use polygraphs to test employees upon hiring or for internal investigations into theft and information leaks. Private clients can order a polygraph test on the website to find out the truth in personal matters, such as adultery. The polygraph may also be used to resolve disputes between relatives, verify the veracity of testimony in family conflicts, or to assess honesty in business relationships. The service is especially popular among people who want to receive objective confirmation of their suspicions or dispel doubts without resorting to legal procedures.
Among whom the polygraph testing service is most popular:
- Corporations and companies;
- Security services;
- Private individuals;
- Government agencies.
10. Is the polygraph not always accurate?
Despite the popularity of the polygraph, its accuracy remains questionable. According to various studies, the accuracy of the lie detector varies from 60% to 90%. This means that errors can occur both in the direction of false positive and false negative results. The reasons may be stress, anxiety, or physiological characteristics of the subject.
Reasons for possible errors:
- False positive results can occur due to excessive stress on an innocent person.
- False negative results are possible if a person is able to control his physiological reactions.
Conclusion
The lie detector is a complex and controversial instrument that has been used for decades in fields ranging from criminology to the corporate world. Despite its popularity, it is worth remembering that the polygraph is not a 100% lie-detection tool. Science and society continue to debate its reliability, but the fact remains that interest in this device has not waned.





