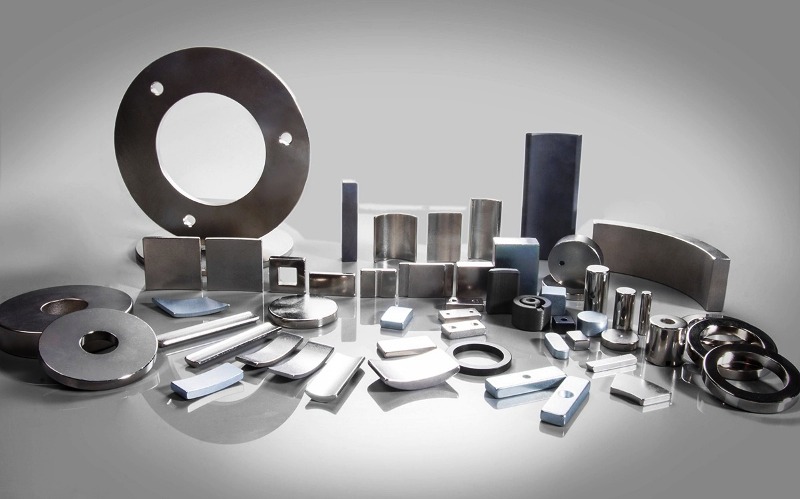
Mysterious and amazing, magnets have fascinated scientists and curious minds for centuries. With their help, we create devices that can navigate in space, lift heavy objects, and even store information. Let's tell you about 10 fascinating facts about magnets that will reveal to you the enchanting world of magnetic fields.
1. Basics of magnetism
Magnets have the property of attracting certain materials, such as iron, nickel and cobalt. This property was discovered in ancient Greece, but it was not until the 19th century that scientists established the connection between electricity and magnetism, which led to the theory of electromagnetism.
2. Earth magnet
The Earth itself is a huge magnet with north and south magnetic poles. These poles change their positions slightly over time and even sometimes switch places during a geomagnetic reversal.
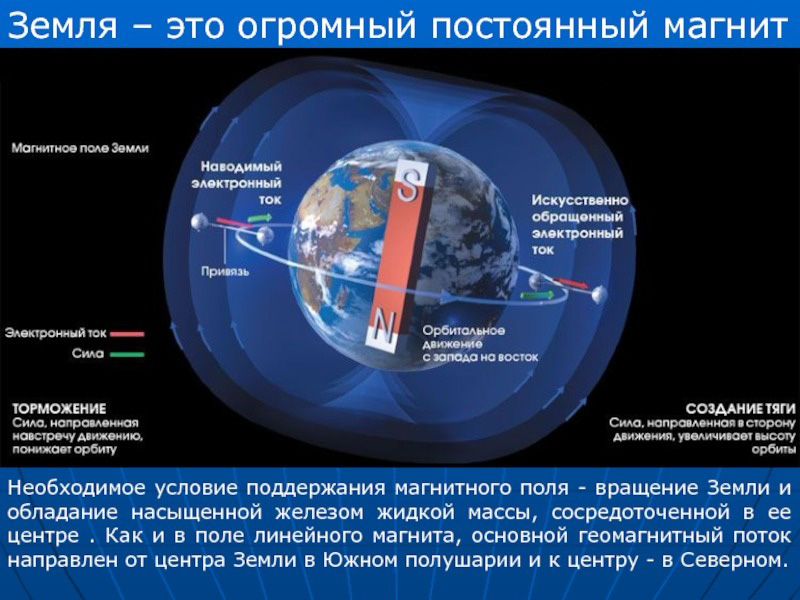
3. Magnetic fields and compasses
Magnetic fields are used to determine direction. The compass, which was originally developed in China, is based on how a needle, when aligned, points to the Earth's north pole due to the influence of its magnetic field.
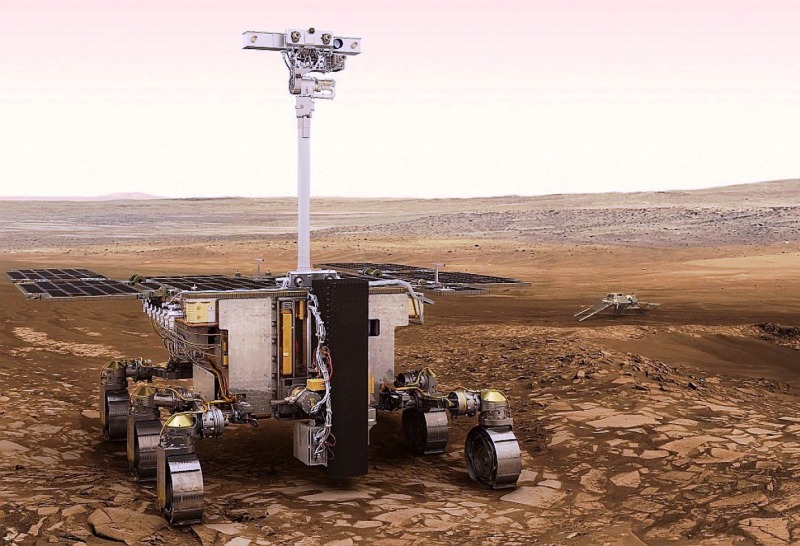
4. Magnets on Mars rovers
The magnets present on the rovers not only perform the role of collecting particles from the surface of Mars, but also play an important role in the study of the planet's atmosphere. The rovers are able to collect small magnetic particles that may contain information about the minerals and chemical elements present in the soil. Analysis of these particles allows scientists to better understand the geological past of Mars, its climate changes, and possible signs of water and life.
5. Quantum magnets
Quantum magnets are nanostructures in which magnetic behavior is caused by quantum phenomena. This section of magnetism is actively studied in modern physics and may lead to the creation of more efficient electronic devices and technologies of the future.
6. Magnets and antimagnets
In addition to what we know about regular magnets, there are also antimagnets. Antimagnets are materials that have the property of being repelled by magnetic fields, while regular magnets are attracted to magnetic fields. The antimagnetic properties are due to the specific orientation of the electron spins in the atoms of the material. This interesting property has led to the creation of various experiments, including magnetic levitation devices in which antimagnets “float” above magnets. This demonstrates some unique aspects of the interaction of magnets and antimagnets that may be used in future technologies and research.
7. Therapeutic use
Magnets have long been considered healing. Today, some people use magnetic bracelets and other products as an alternative therapy, but the effectiveness of this approach remains a matter of debate among doctors.

Although scientific evidence for the health benefits of magnetic therapy remains limited, alternative therapies using magnets continue to gain popularity. In some cases, magnetic bracelets and similar products are claimed by proponents to relieve pain, reduce stress, improve circulation, and even boost the immune system.
8. Temporary magnets
Electromagnets are temporary magnets created when an electric current passes through a conductor. They are widely used in electrical engineering, including transformers, electromagnetic closures, and even MRI scanners.
9. Magnetic recordings
Magnetic materials are used to store information in the form of audio, video, and data on hard drives and magnetic tapes. Information is recorded by changing the magnetic orientation of tiny areas on the surface of the medium.
10. Magnets in living nature
What is interesting is that not only is the magnetic field widely used by humans in technology, but some animals are also able to perceive and navigate using the Earth’s magnetic fields. For example, birds use the Earth’s magnetic field as a compass during migration, helping them find their way over long distances. Some scientific studies also suggest that some animals, such as some species of mollusks and bees, can also use magnetic fields to orient themselves and navigate in the world around them. This amazing phenomenon highlights the deep connection between magnetism and living nature.
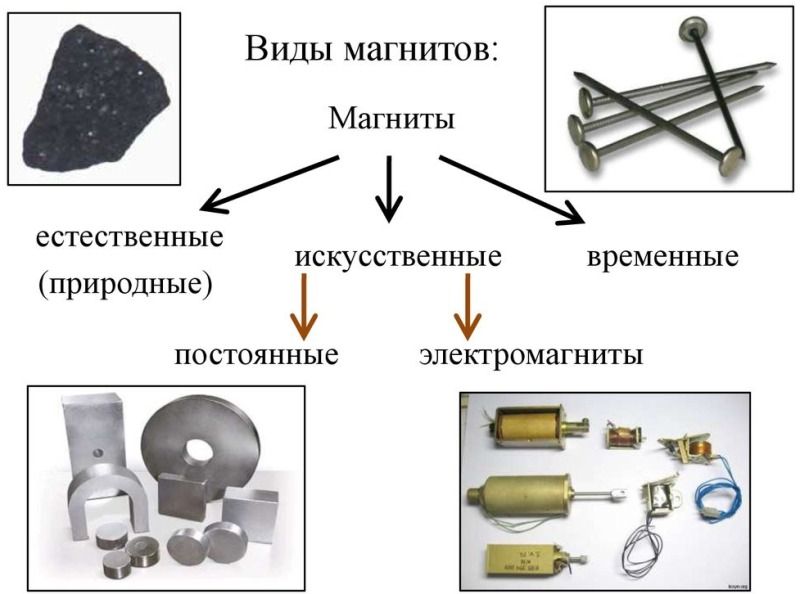
What types of magnets are there?
There are several types of magnets, each with its own unique properties and applications. Here are some of them:
- Permanent magnets: These magnets have a permanent magnetic field and do not lose their magnetic force over time. They are widely used in various fields including electronics, medical devices and mechanics.
- Electromagnets: Electromagnets are created when an electric current flows through a conductor. Their magnetic field can be easily changed by changing the strength of the current. Electromagnets are used in electrical devices such as relays, solenoid valves, and magnetic closures.
- Permanent magnets: These magnets have a permanent magnetic field, but their magnetic force may decrease over time due to various factors. They are widely used in various devices, including dynamos, generators, and speakers.
- Scanning magnets: Used in medical devices such as MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) to create magnetic fields that produce detailed images of the human body's internal organs.
- Solenoids: These are coils of wire wound in a spiral pattern that create a magnetic field when an electric current passes through them. Solenoids are widely used in electrical engineering, medicine, and scientific research.
- Ferromagnetic magnets: These magnets are made from materials with high magnetic susceptibility such as iron, nickel and cobalt. They have strong magnetic properties and are widely used in applications ranging from electronics to magnetic locks.
- Alnico magnets: AlNiCo is an alloy consisting of aluminum, nickel, cobalt, and iron. AlNiCo magnets have high magnetic susceptibility and are used in musical instruments, speakers, and sensors.
- Neodymium magnets: These magnets, also known as NdFeB magnets, are the strongest permanent magnets known. They have high magnetic force and are widely used in modern technology, including strong magnets, motors, speakers and sensors.
This is just a small overview of the various types of magnets. A wider list of all kinds of magnets can be found here in the catalogEach of them has its own characteristics and applications, making magnets an integral part of modern technology and science.

Application of magnets
Magnets play a huge role in various aspects of our lives and modern technologies due to their unique properties. Here are some areas where magnets are widely used:
- Electronics: Magnets are used in the creation of various electronic devices. They are found in speakers, microphones, headphones, loudspeakers, and motors of power tools.
- Energy: Magnets play an important role in the energy industry. Strong magnets are used in generators and electric motors, increasing the efficiency of energy conversion.
- Medicine: Magnets are used in medical technology to create magnetic fields in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, which produce detailed images of internal organs.
- Scientific research: Magnets are used in scientific research, for example, to create high magnetic fields that allow the properties of various materials and phenomena to be studied.
- Transport: Magnetic systems are used in magnetic levitation (maglev) trains to create lift and reduce friction, allowing high speeds to be achieved.
- Data storage: Magnets are used to create magnetic media such as hard drives and magnetic tapes to store data in computers and servers.
- Therapy and diagnostics: Magnetic therapy uses magnetic fields to treat various diseases and pain. Magnets are also used in therapeutic devices, such as magnetic mattresses.
- Industrial production: Magnets are used in industry to lift and move metal objects, which can save workers time and effort.
- Locks and security systems: Magnetic locks are used for security and access control in various buildings and devices.
- Sensors and switches: Electromagnetic sensors use magnetic fields to detect changes in the environment. They are widely used in process automation and security systems.
The use of magnets spans many industries and technologies, from everyday devices to complex scientific research. Their properties make them an integral part of modern civilization.
Magnets are not only toys for children, but also important tools in modern science and technology. They help us understand the nature of magnetism, develop new devices, and discover the great secrets of our planet and universe.













Оставить Комментарий