It is not easy to pinpoint the largest body in the Universe - there is no certainty that we have already explored everything that exists in it.
However, in this article I will rely on existing data and tell you about the largest object in the Universe known to modern science.
The Largest Superstructure in the Universe
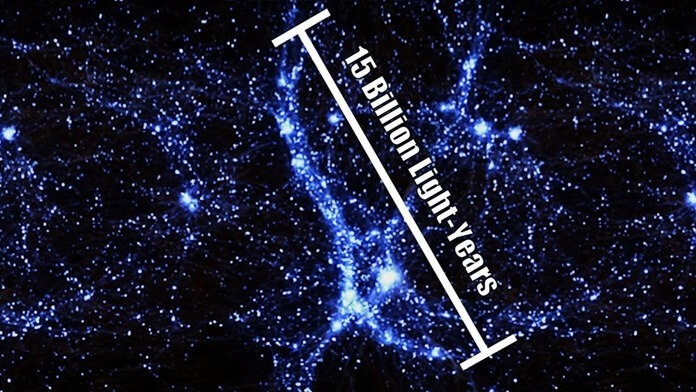
This is the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, or simply the Great Wall. It is located about 10.5 billion light-years away and is a group of an uncounted number of galaxies bound together by gravity.
The galactic filament is estimated to be 10-15 billion light years long. Astronomers discovered this by mapping gamma-ray bursts emanating from this galaxy cluster.
The Great Wall is 7.2 billion light years wide. For comparison, the Milky Way galaxy is about 100,000 light years wide.
"Why does the author call a group of galaxies an object?" the reader might ask. But planets are also considered individual objects, despite the fact that they contain countless different components. On Earth, the individual objects that we use in everyday life are made up of countless atoms, but we still consider them to be single objects.
Simply put, we often ignore the individual components of an object and simply view the entire structure as a single entity. The same is true for galaxy clusters, which, although containing many galaxies, can be viewed as single objects on extremely large scales.
How did scientists find the Great Wall?

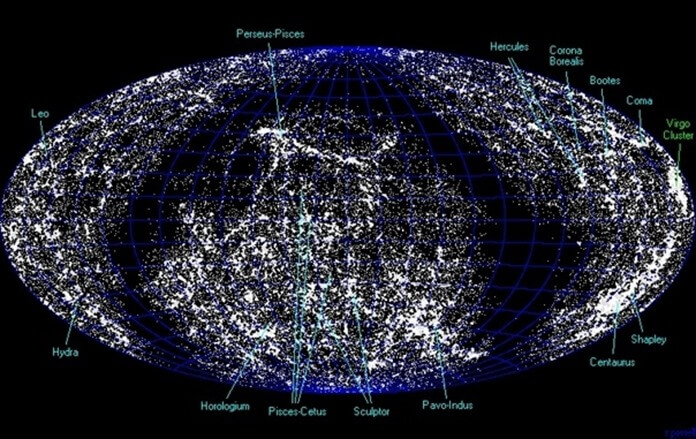
In 2013, a team of scientists studied an anomalously large volume of gamma-ray bursts that were concentrated at a distance of about 10 billion light years, in the direction of the constellations Hercules and Corona Borealis.
- Gamma-ray bursts are the strongest and most powerful form of radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum. This type of radiation is quite rare, and is observed only in a few cases. One such event is a supernova explosion, which releases more energy than the Sun will produce in its entire lifetime.
- The purpose of studying these bursts is that they allow us to detect huge structures in the universe. Studying them allows astronomers to learn a lot about the formation of stars.
- In addition, supernova explosions can lead to the formation of planetary systems such as our Solar System.
Based on data obtained from the SWIFT observatory, the researchers divided the sky into 9 sections. In each section, 31 gamma-ray bursts were studied. In one section, 14 bursts were concentrated in an area with an angular radius of 45° and a red shift of 1.5 to 2.0. This indicates the presence of many (possibly millions) galaxies in this area. This is how an incredibly large object was discovered - the Great Wall.

At first, the researchers could hardly believe what they had found. However, the odds of this set of gamma rays appearing in this location by chance were less than 1%. Because of this, it is reasonable to believe that the Hercules-Corona Borealis Great Wall exists. For this reason, the structure is often called the Great Wall of GRBs.
How does the largest object in the universe defy the cosmological principle?
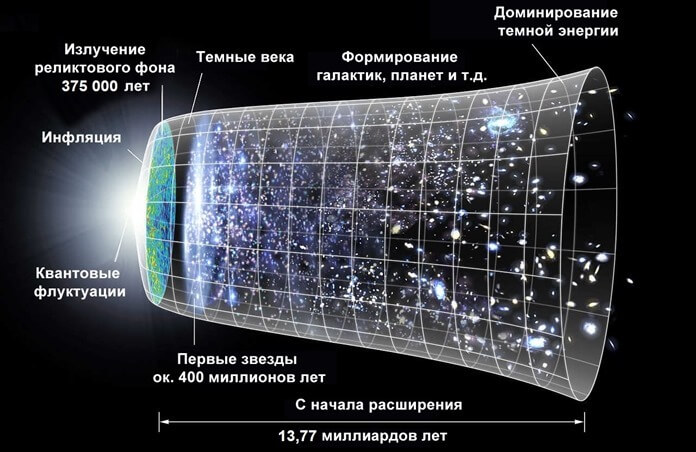
According to the basic assumption of modern cosmology, the universe is very homogeneous. For example, the residual heat from the Big Bang appears to be extremely homogeneous in all directions. Matter in the universe follows the same rule.
- Of course, there is some local heterogeneity in the Universe. For example, there are clusters of stars, galaxies and other matter clusters localized in certain areas.
- But the basic cosmological principle remains: matter in the Universe as a whole is distributed very evenly.
- Otherwise, clumps of matter would begin to attract each other, causing the universe to collapse under its own gravity.
But the cluster of galaxies in the Great Wall is not uniform.
In addition, this giant structure is located at a distance of 10 billion light years, which means that scientists are observing the object as it was 10 billion years ago, or about 3.8 billion years after the Big Bang. And, according to modern models of the evolution of the Universe, such large and complex structures could not have arisen at this stage.
What other large objects are there in the Universe?
- A huge group of quasars – held the record for the largest object ever identified in the Universe until it was broken in 2013. It is a cluster of 73 quasars (massive celestial objects that emit enormous amounts of energy). The structure, located in the constellation Leo, is about 4 billion light-years across.
- There is also a giant ring of 9 gamma-ray bursts, discovered in 2015. This structure is approximately 5.6 billion light-years in diameter. It is believed to be spheroidal or ring-shaped. The distance from this ring to Earth is about 9.1 billion light-years.
- In 2021, an object named "Maggie" was discovered in the Milky Way galaxy. — named after the Magdalena River, the longest river in Colombia. This massive hydrogen filament is 39,000 light years long and is located more than 55,000 light years from Earth. Maggie is five times larger than the largest known gas clouds recorded in modern history.
- South Pole Wall — is a colossus of a huge cluster of galaxies, stretching for a whopping 1.37 billion light years between the constellations of Cetus and Bird of Paradise. The South Pole Wall is special because it is very close to the Milky Way galaxy, only 500 million light years away. And it was discovered relatively recently — in 2020.














Оставить Комментарий