Given how important your brain is, we don't so long it was studied and we still don't know as much about it as we perhaps should. Still, scientists are still working to unravel the mystery of how that fleshy organ in your head controls every aspect of your being, and we’re learning more and more remarkable things about it and about us as a species all the time. It just so happens that some of what’s been discovered about the mind is quite remarkable and, well, mind-blowing.
10. A doctor who studied the brains of psychopaths discovered that he was a psychopath.
Everyone has a brain, but not everyone has the same type of brain. There are a number of neurological conditions and disorders that can alter your consciousness to a greater or lesser degree. And for many years, one of the most fascinating parts of neuroscience and the study of the mind has been the minds of criminals, especially people like serial killers and psychopaths.
Of course, not every psychopath is a serial killer, and even that distinction is part of the research. Why do some psychopaths become killers and others just leaders ?
James Fallon of the University of California studied the minds of psychopaths as part of his work in the psychiatry department. The lab where he worked had been doing actual brain scans of serial killers over many years as part of their criminal defense. And Fallon, as a psychiatrist, studied these scans and began to notice certain patterns. He used this as a starting point and became something of an authority on the mind of a psychopath. And that's when things got weird.
Delving into his family history, Fallon uncovered a number of questionable relatives, including a notorious murderer Lizzie Borden . He and his family later participated in some Alzheimer's studies that required brain scans as controls. Fallon later saw his own scan and immediately recognized it. It was psychopath brain .
Fallon, of course, had never killed anyone, and he thought it was stupid until almost everyone in his life agreed that, yes, he was a little crazy. Manipulative, reckless, emotionally distant, but able to feign empathy. It made sense. How did Fallon respond? He was trying to practice being good, and he admits he has dark tendencies, but not necessarily dangerous ones.
9. Scientists have suggested that dolphins are considered non-human creatures

One of the fun things about studying the brain is that you don't just have to study humans. Researchers studying dolphins, arguably the smartest creatures in the world after us, have made some impressive discoveries over the years about just how smart these animals are. And perhaps the most stunning conclusion any researcher has come to is that the dolphin deserves to be considered human, non-human .
What is a non-human? Pretty much what it sounds like. Psychologists at the City University of New York and zoologists at Emory University scanned the brains of dolphins and observed their behavior to determine that the animals possess with a distinct character , self-awareness, the ability to foresee the future, and the ability not just to learn but to teach others. They are people, just not people.
Efforts have been made to ensure that dolphins and whales are recognized as a person and therefore individual rights since the publication of the study. In 2013, India announced , that dolphins can no longer be used in circuses and shows like Sea World, although it did not grant them human rights. .
8. LSD activates unusual parts of your brain for visual processing.

If you've ever taken LSD, you may not need to know what science says it does to your brain, but when you start tripping, some amazing things happen. And when you think you're seeing things, your brain agrees with you.
Brain scans done on people who took LSD specifically to see how it affected their brain activity have produced some instructive results. Parts of your cortex that are normally buffered and protected from information overload overloaded signals. The temporal cortex receives less information than usual, while the posterior cingulate cortex receives too much.
Normally your thalamus passes information to other parts of your brain, but LSD disrupts that ability, causing unusual feelings and sensations. There are many things that happen that your thalamus normally protects you from because you don't need to experience them.
By taking the drug, you can process new visual signals in the parts of your brain that usually not related with visual processing, which is what happens when you start hallucinating. The exact way this all works is still unknown.
7. Love and cocaine affect your brain in very similar ways.

If you've ever heard the expression "drunk in love" or observed yourself or others acting weird when you're in love, it's not just a joke. Your brain really does go a little crazy when you're in love, and research has shown that love and cocaine have a very similar effect.
This isn't about long-term attachment, but rather the early euphoric feeling that people sometimes experience in new and intense relationships. This explains why some people overdo it and do weird impulsive things, like getting married the day after meeting someone.
Both love and drugs like cocaine work on the same pleasure centers in your brain that give you a sense of satisfaction. In fact, the way your brain processes love and pain relief , very similar. Both give you that rush of dopamine that makes everything feel great.
6. Men who wear ties get less blood to the brain

A tie is one of those items of clothing that serves no real purpose, but people continue to wear them more out of tradition than anything else. They are considered formal and businesslike. But there is some evidence that they do not do your brain any good, due to their tendency to limit blood flow .
Obviously, you shouldn't strangle yourself to death with a tie, but the fact remains: it's essentially a noose that you're freely choosing to strangle yourself with. The result is less blood flow to your head and brain. Researchers scanned the brain 15 men before and after wearing a tie. Blood levels in the brain were reduced by about 7.5% after tightening the tie. A small amount, sure, but how much blood do you want to deprive your brain of?
The study concluded that the reduced blood flow may not be life-threatening, but could have more serious consequences for smokers and people with high blood pressure. Earlier studies have shown that ties Also can spoil the eyes .
5. Murderers tend to have less grey matter than other criminals.

We've already touched on the brains of psychopaths, but what else is going on in the brains of killers? Not every psychopath is a killer and not every killer is a psychopath, but research 800 convicts showed some interesting results. The brains of murderers in particular were different from other brains. Specifically, those who had committed murder or attempted murder had reduced gray matter compared to those who had been incarcerated for other crimes.
Not surprisingly, these reductions were seen in brain areas associated with behavior control and emotional processing Less gray matter means they are less able to process information related to these things.
Those who might have suffered from things like psychosis or schizophrenia, as well as those who might have had head injuries, were excluded from the study, ruling them out as potential causes of what was observed.
4. Almost every NFL player studied has a degenerative brain disease.

It’s no secret that professional football is a physical game, and the risk of injury can be high. But no player who signed up in the past fully understood the risks, which are far less obvious than simple bumps and bruises. Brain scans of many former NFL players have shown a high prevalence of chronic traumatic encephalopathy, or CTE.
At least at 320 players have been diagnosed with the degenerative brain disease, and at least two dozen people, most in their 20s and 30s, have died as a result. A 2017 study of 111 NFL players found the disease in 110 of them .
The condition, historically associated with boxers, causes far more damage than meets the eye. Men who suffer from the condition don’t just have a disease that kills them, it’s a condition that changes their personality. Some of the victims have committed suicide, while others, like Jovan Belcher, Phillip Adams and Aaron Hernandez, have killed others before taking their own lives.
3. The brains of marijuana smokers show abnormalities

Marijuana has become very popular in the last few years as more and more places have legalized its use. A number of states and countries support smoking marijuana or otherwise using cannabis, and many proponents have argued for years that weed is much safer and better for you than things like alcohol or tobacco. But unsurprisingly, increased use has led to more research, and there are some studies that suggest it’s not as good as everyone hopes.
In 2022, the American Heart Association took a fairly neutral stance, suggesting that it is necessary to carry out additional research effects of marijuana on the brain. Rodent studies show that marijuana use can impair memory, learning, and brain development. Human studies, however, produce results that are all over the map, with more or less favorable results depending on the test, which doesn't really help anyone.
A 2014 Harvard study found that marijuana smokers, even casual ones, had significant abnormalities in the parts of the brain that control emotions and motivation . Is anyone shocked to hear that marijuana smokers are unmotivated? Probably not. But it could become an even bigger problem as marijuana use becomes more widespread.
2. Space travel changes the shape and other aspects of your brain

Space is not a natural environment for humans, and our bodies have some curious reactions when we remain in zero gravity. One of the most curious side effects, which has been discovered by the Russian space program, is that long-term spaceflight can change the shape and function of your brain.
Researchers who studied the brains of astronauts noted that the brain was significantly reprogrammed They scanned the brains of 12 astronauts before and after their time in space, averaging 172 days per astronaut.
Cerebral fluid, white and gray matter were changed after spaceflight. Parts of the brain actually change shape to adapt to the zero-gravity environment, but they don't immediately change back when astronauts return to Earth. In fact, months later, the changes are still present, and it's not entirely clear what effect they might have in the future.
1. Scientists have studied the brains of monkeys and have managed to extract faces from their thoughts
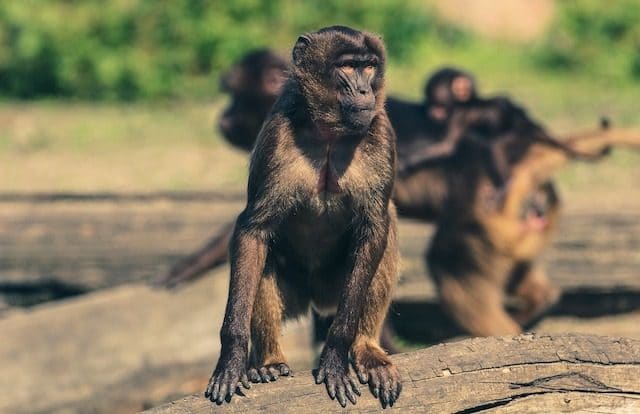

We studied the brains of dolphins to determine that they are not human, so what could we learn from the brains of monkeys? Something out of science fiction.
Researchers at the California Institute of Technology studied the brains of monkeys and how they process things like the faces they see. As a result, they were able to determine how neurons in the brain organize information when a monkey sees a face and then extract that information. In other words, they were able to reconstruct face , which the monkeys saw, based solely on the information in their brains. When the reconstructed faces were compared to real photographs of the people, the results were nearly identical.
The scientists weren't specifically trying to read the monkey's brain, but it actually came about as a result of research into algorithms for technologies face recognition . And it turned out that the algorithm worked almost exactly the same way as the monkey brain.
While these results have the potential to improve facial recognition technology, there are also some more esoteric possibilities, such as perhaps using a murder victim's brain to see the face of their killer.














Оставить Комментарий